Address:7th Floor, Gaofeng Building, Dalang Street, Longhua District, Shenzhen
Website:www.longstartech.com.cn
TEL:0755-2556 9680
FAX:0755-2556 6650
Mobile:13316929948(同V)
Email:James@longstartech.com.cn
Contact Person :James
Temperature and time are the most critical factors for hot curing and baking. The quality of finished products depends on these two parameters. Similarly for UV curing, curing effect depends on two factors - irradiance and time. Not enough time, uv curing may not be complete, curing effect is affected. In fact, the combination of irradiance and time is so important that energy density measurements are made almost always during UV curing.
(note: the importance of energy density value does not mean that other parameters are not important during curing, such as irradiance value, spectral wavelength, and coating thickness are also critical.)
Mathematically, the energy density can be thought of as the area under the radiation curve measured over time, as shown below.
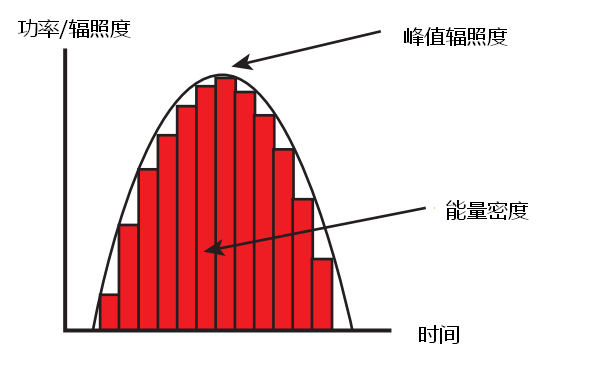 The region under the curve is called an integral, and one way to find that region is to break it down into long, thin rectangles and add them together. Clearly, the narrower the rectangle, the more precisely the area can be measured without missing the peak irradiance value. Measuring energy density depends on a number of radiometers (early called "integrated radiometers").
The region under the curve is called an integral, and one way to find that region is to break it down into long, thin rectangles and add them together. Clearly, the narrower the rectangle, the more precisely the area can be measured without missing the peak irradiance value. Measuring energy density depends on a number of radiometers (early called "integrated radiometers").
The instrument takes several radiation samples per second and adds these values. By speeding up the sampling rate to achieve high resolution and accurate irradiance calculation, the consistency of energy density calculation can be achieved. The more samples collected at the same time, that is, the narrower the "rectangular frame", the higher the measurement accuracy. Today's radiometers on the market can process hundreds (or even thousands) of times per second, and each manufacturer processes different amounts of data. This leads to different manufacturers of irradiators to measure the same light source, but the results are inconsistent.
But as you're measuring, other devices are changing. Some LED electronic control systems use PWM technology. When using PWM, the power supply voltage will be turned on and off rapidly to change the output of the light source. As shown in the figure below, the LED's on-off speed is very fast, which is imperceptible to human eyes. In many curing processes, this technology performs very well.
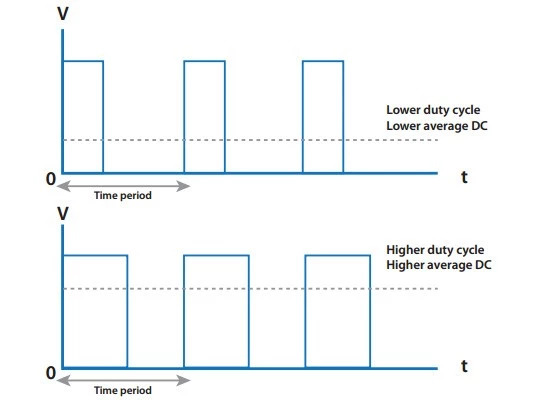 PWM can be used to change the output power of the array, and the switching off and on of the light source is very fast, but it brings great challenges to the irradiometer measurement sampling. It's a bit like having a camera shoot a rotating fan blade. The sampling energy density reading may not accurately reflect the actual measurement results, and it may be higher or lower than the true value according to the algorithm used to calculate the irradiance and energy density.
PWM can be used to change the output power of the array, and the switching off and on of the light source is very fast, but it brings great challenges to the irradiometer measurement sampling. It's a bit like having a camera shoot a rotating fan blade. The sampling energy density reading may not accurately reflect the actual measurement results, and it may be higher or lower than the true value according to the algorithm used to calculate the irradiance and energy density.

